What is the ‘Hero Myth’? How is this Evident in Modern Management and Leadership Discourse?
Unit 2 Essay – Graduate Certificate in the Psychology of Risk, Australian Catholic University.
Lecturer: Dr Robert Long
By: Andrew Thornhill
Introduction
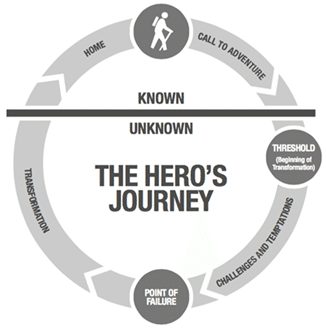 The hero myth, appearing in writing since 380BC[1], describes a narrative of an individuals’ heroic journey through readily recognisable steps, from a call to adventure, challenges and a transformational return[2]. Despite widespread belief and incorporation in modern leadership discourse, using heroic attributes to predict leadership capacity has been empirically demonstrated to be a myth[3].
The hero myth, appearing in writing since 380BC[1], describes a narrative of an individuals’ heroic journey through readily recognisable steps, from a call to adventure, challenges and a transformational return[2]. Despite widespread belief and incorporation in modern leadership discourse, using heroic attributes to predict leadership capacity has been empirically demonstrated to be a myth[3].
Drawing on the work of Haslam, Reicher, and Platow[4], Minztburg[5], Sinclair[6] and Long and Ashurst[7], this essay explains the hero myth and the process of how the metaphor of heroic leadership has found widespread acceptance in modern leadership writing, development and discourse. The nature of the heroic leadership discourse is also analysed, with respect to language, imagery, power arrangements and discussion, with particular reference to what is, and is not, said and who benefits from the discourse.
The limitations of the hero model for effective leadership are discussed with particular reference to leadership in risk. In particular, conclusions are made about the trajectory that an inherently individualistic model of leadership can put an organisation on.
The Hero Myth
Haslam, Reicher and Platow cite the example of the great man myth in Plato’s Republic dated 380 BC[8]. Flowers contends that there is no distinction between the leader and hero in early stories, because leadership was usually a function of heroism in war[9].
The common structure of the hero’s journey: a call to adventure; crossing of a threshold; challenges and temptations; a supreme ordeal or failure; a transformation; and a return – is identified by a range of authors including Flowers[10] and Long and Ashurst[11].
So how has the hero myth become such a dominant metaphor in modern leadership books, development and discourse? Thomas Carlyle’s influential series of lectures on Heroes and Hero Worship, delivered in 1840, strongly attributed special characteristics to leaders[12]. Haslam, Reicher and Platow[13] identify that from an early age we are told stories of great leaders, whilst Hook argues that in most countries “the cult of the hero and leader is sedulously developed for adults as well as children and students”[14], potentially enabling a conditioned acceptance of the myth in later in life. The unconscious need of followers for psychological security and strong leadership[15] to save them from perceived difficulties can reinforce, or be exploited by, the heroic leader, a process Sinclair terms “the seduction of leadership”[16]. This need for psychological security intensifies during a crisis[17].
Do the attributes of heroic leaders enable a capacity for greater leadership? A 1959 study by Richard Mann evaluated attributes commonly associated with heroic leaders (intelligence, adjustment, extroversion, sensitivity, masculinity, conservatism and dominance) and empirically demonstrated that any correlation between these attributes and leadership capacity was, at best, weak[18]. Mintzberg reviewed the performance of nineteen graduates of the 1990 Harvard University program who had been identified as having “made it to the top” in corporate roles. Fourteen had left or been dismissed following poor or questionable performance[19]. Minztberg also reviewed the results of a 1999 article by Charan and Colvin that reviewed the failure thirty-eight CEOs[20].
Despite any factual basis, the heroic leader has become the dominant paradigm in leadership[21], particularly leadership in risk[22]. Sinclair[23] argues that it can be “difficult to stand outside that regime and question it” whilst, similarly, Haslam, Reicher and Platow note that “its intellectual shackles are both tight and heavy”[24]. Sinclair provides insight into the process by which myth becomes accepted wisdom – by the discourse framing and limiting understanding of what leadership can be and persistently and habitually canonising heroic leadership[25]. From a social psychology perspective, commitment to a leadership approach based on assumptions is an example of groupthink. The sunk cost of investment in heroic leadership can create further resistance to change within an organisation.
In subsequent sections this essay discusses how the hero myth is evident in modern management and leadership discourse and the limits of an inherently individualistic approach to leadership in risk.
The Hero Myth in Modern Management and Leadership Discourse
The dominant view of the heroic leader is evident in modern leadership discourse, including how leadership is written about, discussed and power arrangements. This section identifies this discourse, including what is overtly written or stated, what is hidden, the meaning carried by the words, power arrangements and how the discourse can frame and prime perceptions of what leadership is[26] and could be[27].
Leadership writing often reflects a traditional hierarchical approach to leadership, founded in the hero myth and led by an individual with the right attributes. Long and Ashurst identify an overwhelming majority of 120,000 books returned in an Amazon search for ‘leadership’ as reflecting this traditional view of leadership[28]. Similarly, Haslam, Reicher and Platow report 80,000 results when typing the phrase “the leadership secrets of” into a search engine[29]. Flowers identifies the consistent theme of individuals bravely following their own dreams in books and tapes on leadership[30]. Mintzberg[31], Bligh and Kohles[32] and Hook[33] all identify a tendency to attribute achievements to an individual leader even where there is no direct evidence to support this belief. Similarly, Sinclair argues that “CEOs magnified by media profile – have come to represent leadership, to speak for it, to be held up as experts in it”[34] and that the extent of writing on heroic leadership, citation of big name companies and endorsement of well-known people create a “weight of authority”[35].
Mintzberg reports on a similar perception in MBA programs – that of the inherent superiority of the abilities of managers – “a professional managerial caste that considers itself trained – and therefore destined – to take command of this nations corporate life”[36]. Sinclair notes “palpable hostility” from a group of executive MBA students when teaching a unit based on reflection, experiential learning and critical perspectives on leadership[37]. Sinclair argues that the leadership development industry “sits within a regime of truths supported by interlocking systems of expert and economic power”[38]. Those who profit from leadership development and writing have a vested interest in promoting heroic leadership over alternate models of leadership[39].
This discourse of heroic leadership is inherently individualistic, about self and centralisation of power to an individual – with limited reference to the perceptions, needs or contribution of followers. The discourse is about leadership and control over others, rather than with others[40], by a leader with the superior attributes, reinforced by the imagery of a hero leading others against all odds.
What is not said is as informative as what is said. A clear omission from the discourse of heroic leadership is the role of women[41] [42], or others perceived as not having the right attributes. This is in contrast to the empirical research of Mann who found no association between heroic attributes and leadership ability[43]. Similarly, Mintzberg cites numerous of examples of male leaders who have created substantial damage to the Organisations they led[44]. In contrast, Fletcher notes that relational attributes, identified as important in post-heroic leadership models – such as empathy, community and collaboration, are culturally assigned as feminine[45].
Power arrangements inherent in the discourse are also not stated. The hero myth centralises power to the individual and dissent is not tolerated[46]. The power is transmitted through the leaders’ vision in to systems, rules, procedures, internal regulations and are reinforced through selection procedures, succession planning, performance reviews and personality testing[47]. Sinclair describes a cyclic process, whereby aspiring leaders need to be compliant and perform within the accepted structure and tools of leadership[48].
Not only is dissent from the vision of the leader not tolerated, power structures are reinforced through an in/out group mentality and binary opposition[49]. The tendency to not question or raise counter opinions to the leader can be further entrenched by an individuals’ obedience to authority – where the pain caused by cognitive dissonance of not belonging to the group is greater than the pain caused by disagreeing[50].
The language supporting the dominant paradigm in safety risk leadership (zero, control, compliance, non-compliance, requirements, systems, hierarchy of control, penalties, regulation) identify, normalise and prime a discourse and ideology of control, power, non-questioning and a system of thought whereby the transformational leader and regulator are focussed on saving idiots from their own mistakes. The discourse in safety leadership creates an appearance of involvement and consultation whilst providing limited input by followers and masking what is not said (engagement, people, learning, relationship, you don’t have any power). As Long and Ashurst note[51], the hero myth is represented even more starkly in risk related leadership literature. Sinclair describes the cyclic nature of the power arrangements, whereby “only those most compliant to the overall purposes of the organisation rose to the top”[52]. The discourse of control and fear[53] is also reflected in the power, communication and language of regulators[54].
The critical question of the trajectory this discourse sets an organisation on is further discussed in the next Section.
Limitations of the Hero Myth for Effective Leadership in Risk
Long and Ashurst contend that the hero myth is represented more starkly in literature relating to risk management[55]. This section examines the limitations of the heroic approach to leadership in risk, how it can enable significant risk events and the trajectory it can set an organisation on.
The individualistic nature of the hero model is inadequate for managing the complexity and dynamic nature of risk in a modern business context[56] [57], and as Sinclair argues, “impedes meaningful public engagement with the complexities of political and social reality”[58]. It a model that relies on the assumed powers of an individual that simply do not match reality[59]. The individualist model almost inherently limits cultural change because, as Long notes, culture is determined by the group[60] and ignores the expert knowledge of those performing workplace tasks that create risk.
Haslam, Reicher and Platow identify heroic leadership as an old psychology and articulate a new, relational model[61]. Sinclair also argues that leadership is socially constructed and relational[62]. Similarly, Long and Ashurst suggest a relational following-leading approach to leadership in risk[63], whilst Long identifies a hidden social contract between leaders and followers, which provides leaders with, and can remove, their moral authority[64].
Haslam, Reicher and Platow identify that cults of personality often enables corruption[65], or actions that set the organisation in a direction that creates significant risk with limited oversight or accountability[66]. Similarly, Sinclair cites the centralisation of power at Enron, prior to its collapse, as a “sort of collusive seduction, which can become so powerful as to forestall any criticism”[67]. This seduction of followers by leaders, in conjunction with obedience to authority, has enabled leaders such as Hitler and Mussolini to exploit followership for evil purposes[68]. The transfer of such substantial power to an individual also creates unrealistic expectations of the individual and can enhance their sense of infallibility, inflexibility, entitlement and a perception of themselves as outside the constraints applied to ordinary people[69].
The discourse of heroic leadership creates a hidden trajectory of perfectionism, self and control – leaving no room for human judgement[70]. However, the outcomes are predictable – the creation of in/out groups, under reporting (such as the creative management and recording of potential lost time injuries)[71], lip service and a tick and flick approach to compliance, subversion, scepticism[72] and a preclusion of culture change – which is determined by the group[73].
Conclusion
Despite the predictable outcomes of a perfectionist trajectory, and heroic leadership being a demonstrated myth, heroic leadership continues as the dominant paradigm in leadership, particularly leadership in risk.
Why organisations continue on this trajectory is, in some cases, simply a lack of understanding of social psychology. Even where the limitations and risk of the hero model are recognised, change can resisted by those in power, through the dissonance and sunk cost associated with admitting failure in a strategy and through a tendency to stick with a dominant paradigm that is normalised and accepted as fact.
Alternate models, identifying the fundamental social and relational nature of leading rather than just leadership, provide a model more suited to management of risk in complex business environments. They also enable harnessing of the expert knowledge of the group and facilitate commitment and human judgement in risk.
Bibliography
Download the full essay for bibliography:
Download Essay: The Hero Myth


Do you have any thoughts? Please share them below